Smart locks revolutionize access control by combining traditional locking mechanisms with advanced technology. These locks offer convenient, secure, and customizable ways to manage entry to your home or property. This exploration delves into the working principles of smart locks, addressing their communication methods, authentication processes, user management, remote access, integration with smart home systems, and potential vulnerabilities.
Communication Methods:
Smart locks rely on various communication methods to interact with users and other devices:
1.Bluetooth: Many smart locks use Bluetooth to connect directly with smartphones or tablets in close proximity. This method is ideal for short-range interactions and doesn't rely on an internet connection.
2.Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi-enabled smart locks communicate with your home's wireless network, allowing remote control and access from anywhere with an internet connection.
3.Zigbee and Z-Wave: These wireless communication protocols enable smart locks to connect with other smart devices within a home automation ecosystem, promoting seamless integration.
Authentication and Access:
Authentication is at the core of smart lock functionality, ensuring secure access control:
 1.PIN Codes: Users enter a personalized PIN code on a keypad integrated into the lock. The correct code grants entry.
1.PIN Codes: Users enter a personalized PIN code on a keypad integrated into the lock. The correct code grants entry.
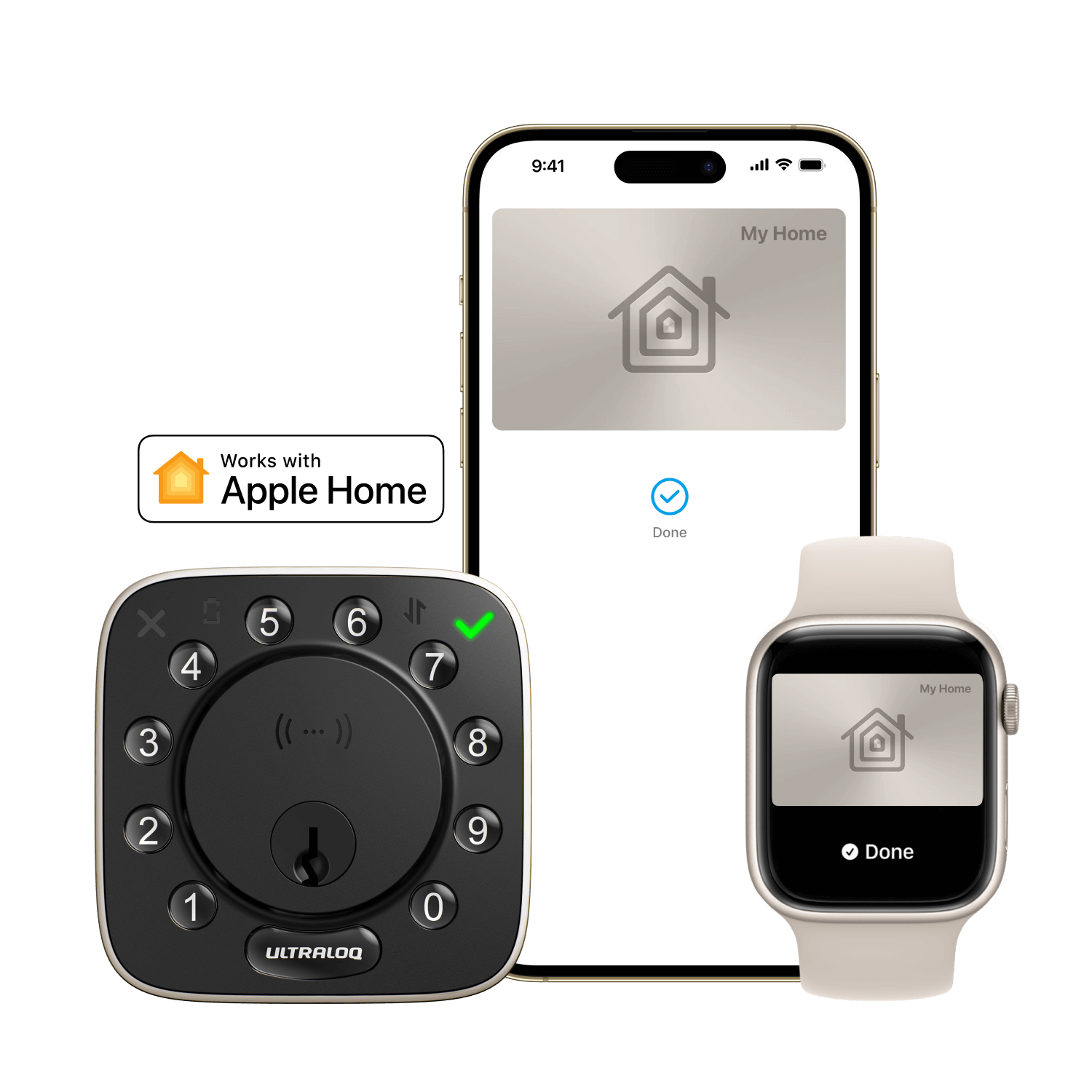
2.Biometric Scans: Some smart locks offer biometric authentication, using fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice recognition to verify the user's identity.
3.Smartphone Apps: Smartphone apps linked to the smart lock allow users to lock or unlock doors remotely. Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connections facilitate this communication.
4.Physical Keys: Some smart locks retain traditional key access alongside digital methods for added flexibility.
Remote Access:
One of the defining features of smart locks is remote access:
1.Smartphone Apps: Remote locking and unlocking are facilitated through smartphone apps. Users can grant access to guests or service providers from a distance.
2.Virtual Keys: Temporary access can be granted using virtual keys, which can be sent to recipients via the app and revoked after use.
User Management:
Smart locks provide extensive user management capabilities:
1.Temporary Codes: Owners can create temporary access codes for guests, service providers, or renters. These codes can have expiration dates for added security.
2.Scheduling: Smart locks allow users to set schedules for when certain access codes are active. For example, a code can be valid only during specific hours of the day.
Integration with Smart Home Systems:
 Smart locks seamlessly integrate with broader smart home setups:
Smart locks seamlessly integrate with broader smart home setups:
1.Smart Home Hubs: Integration with smart home hubs or platforms like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, or Apple HomeKit allows for centralized control of smart devices.
2.Automation: Smart locks can be part of automation scenarios. For instance, when you unlock the front door, the lights can turn on automatically.
Security Measures and Vulnerabilities:
Smart locks prioritize security to prevent unauthorized access:
1.Encryption: Secure communication between the lock and controlling devices is ensured through encryption, safeguarding data.
2.Physical Durability: Smart locks are designed with anti-tampering features and durable materials to resist physical attacks.
3.Firmware Updates: Regular updates address security vulnerabilities, enhancing protection.
In Conclusion:
Smart locks offer an innovative approach to access control, utilizing a combination of authentication methods, communication protocols, and integration with smart home systems. They grant users keyless entry, remote access, and robust security features. By understanding the workings of smart locks, users can harness their benefits while safeguarding against potential vulnerabilities.